15 Warning Signs That You Are Eating Too Much Protein
Protein is an essential part of a healthy diet, helping to build and repair tissues, muscles, and other important parts of our bodies. However, too much of a good thing can sometimes cause problems, and protein is no exception.
Overloading on protein, whether from food or supplements, can lead to a range of health issues that might be holding you back from feeling your best. Here are several warning signs that you might be eating too much protein and should reconsider your diet.
Feeling Constantly Thirsty
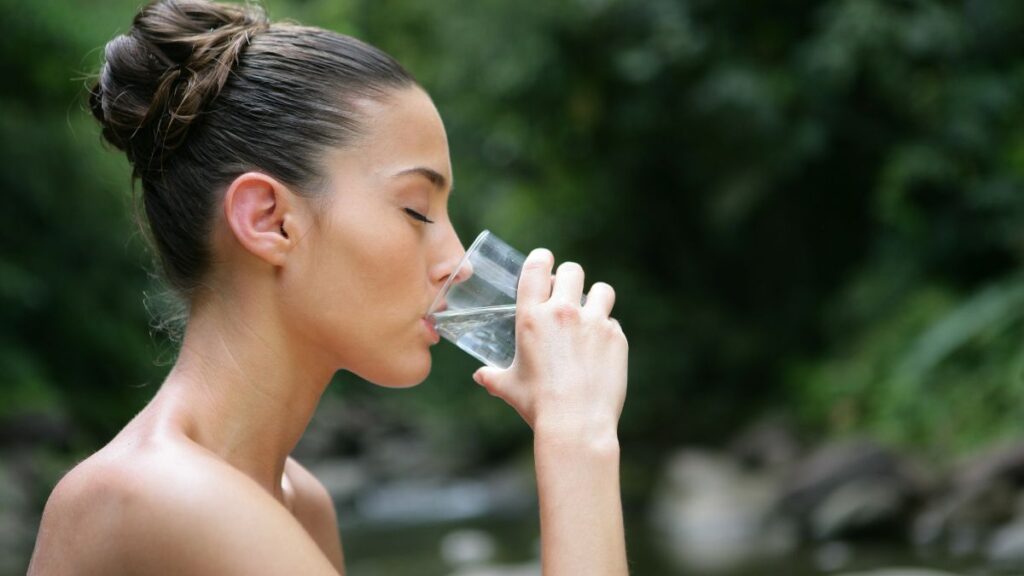

One of the first signs that you may be consuming too much protein is constant thirst. A high-protein diet forces your kidneys to work harder to process and remove the excess nitrogen found in proteins, which leads to more water loss.
As a result, you might find yourself feeling thirsty more often than usual. Drinking more water is essential, but if you’re always thirsty despite staying hydrated, consider cutting back on protein. Balance is vital to staying healthy.
Unexplained Weight Gain

While protein is often seen as helpful for weight loss, eating too much can have the opposite effect. Protein-rich foods can be high in calories, and over time, those extra calories can lead to weight gain, especially if you aren’t active enough to burn them off.
It’s important to pay attention to portion sizes, even with healthy protein sources. Protein overload could be the culprit if the scale starts creeping up despite your efforts.
Frequent Constipation

Eating too much protein can sometimes result in constipation. High-protein diets often lack fiber, which is necessary for healthy digestion. If you eat a lot of meat, eggs, and dairy but not enough fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, your digestive system may slow down.
To prevent this, balance your protein intake with plenty of fiber-rich foods like vegetables and whole grains. Your gut will thank you.
Bad Breath

A high-protein, low-carb diet can lead to an unpleasant side effect: bad breath. When you consume a lot of protein and cut back on carbs, your body may enter a state called ketosis, which burns fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
This process produces chemicals called ketones, making your breath smell less than fresh. Even brushing your teeth may not help much, as the smell is deep within your body. To combat this issue, consider reducing protein and increasing healthy carbs.
Constant Fatigue

If you’re feeling unusually tired despite getting enough sleep, it could be a sign that you’re eating too much protein and not enough carbs. Carbohydrates are your body’s primary energy source, and when they are too low, your body might not have enough fuel to keep you energized.
A diet too high in protein and too low in carbohydrates can leave you feeling sluggish and drained. To maintain balanced energy levels, make sure to include healthy carbohydrates like fruits and whole grains.
Dehydration

Protein metabolism requires a lot of water, which means your body loses more fluids when you’re eating too much of it. If you’re consuming more protein than your body needs, you could become dehydrated even if you’re drinking what seems like enough water.
Dry skin, dizziness, and headaches are symptoms of dehydration. If you notice these signs, try reducing your protein intake and drinking more fluids to see if the problem improves.
Trouble Sleeping

Too much protein, especially late in the day, can make it harder for your body to wind down for sleep. Protein takes longer to digest than carbs or fats, which can cause your body to stay more active internally when it should be resting.
A lack of carbohydrates can decrease the production of serotonin, a hormone that helps you relax and sleep. If you’re having trouble falling or staying asleep, try reducing your protein intake at dinner and adding more balanced carbs.
Mood Swings

High-protein, low-carb diets can affect your mood. Carbohydrates play a big role in producing serotonin, the brain chemical responsible for making you feel happy and calm.
Without enough carbs in your diet, your serotonin levels may drop, leading to irritability, anxiety, or mood swings. While protein is essential, it’s important to include complex carbs like whole grains and fruits to maintain emotional balance.
Increased Body Fat

If you’re eating too much protein, especially from sources high in fat like red meat and full-fat dairy, you could be storing excess calories as fat. Protein can turn into fat if it’s consumed in excess and not burned off through exercise.
This extra fat often collects around the belly area, leading to unwanted inches around your waist. A balanced diet with moderate protein, healthy fats, and plenty of vegetables can help you maintain a healthy body composition.
Digestive Issues

If you’re experiencing bloating, gas, or other digestive problems, it could be a sign of too much protein in your diet. A lack of variety and fiber in a protein-heavy diet can cause your digestive system to slow down or become irritated.
Many people who consume a lot of protein from dairy products like cheese or whey protein also experience discomfort if they are lactose intolerant. To avoid these issues, balance your protein with more plant-based foods and fiber.
Kidney Strain
Eating too much protein can strain your kidneys. When you consume excess protein, your kidneys must work harder to eliminate waste products from protein metabolism, particularly nitrogen.
Over time, this can lead to kidney problems or exacerbate existing issues, especially if you have a history of kidney disease. Keeping your protein intake within recommended levels is important to protect your kidneys from unnecessary stress.
Nutrient Deficiencies

A diet that’s too focused on protein can lead to nutrient deficiencies. If protein-rich foods crowd out other important foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, you may not get enough essential vitamins and minerals.
This imbalance can lead to deficiencies in fiber, vitamin C, and other nutrients crucial for overall health. To stay balanced, eat a variety of foods from all the food groups.
Muscle Cramps

While protein is key for building and maintaining muscle, eating too much of it can sometimes lead to muscle cramps. This is often due to dehydration, as the body needs more water to process protein.
When you don’t drink enough water to compensate, your muscles may start to cramp. If you’re noticing more cramps after a workout or during the night, try cutting back on protein and increasing your water intake.
Frequent Hunger

Oddly enough, eating too much protein can leave you feeling hungry, especially if you’re not getting enough fat or carbs. Protein alone isn’t as satisfying as a meal with balanced macronutrients.
Without enough fat and carbs, you may feel unsatisfied and continue to snack, leading to overeating and weight gain. The best way to keep hunger at bay is to eat a balanced plate with protein, healthy fats, and whole grains.
Heart Issues

While lean protein is great for your heart, too much protein from sources high in saturated fat, like red meat and full-fat dairy, can increase your risk of heart disease. Saturated fats can raise cholesterol levels, which can clog your arteries over time.
If you eat many of these protein sources, it is important to limit your intake and focus on heart-healthy options like fish, beans, and lean poultry.
15 Pizza Recipes That Will Transcend You Into Cheesy Heaven

Pizza is a universal love that comes in various styles with countless topping options. From traditional pepperoni to keto options, this list has a favorite pizza recipe for everyone. Enjoy!
15 Pizza Recipes That Will Transcend You Into Cheesy Heaven
15 Innocent-Looking Vegetables That Are Junk Food in Disguise

When we think of vegetables, we often imagine healthy, nutrient-rich foods that benefit our bodies. However, not all vegetables are as healthy as they seem. Some innocent-looking vegetables can become junk food when prepared or served in unhealthy ways.







